Primero deslizamiento :
Ponemos el paciente en decubito prono.
El fisio esta al lado homolateral del paciente.
 Fijamos el pelvis y el acetabulo con una banana.
Fijamos el pelvis y el acetabulo con una banana.
Ponemos nuestras dos manos sobre la cabeza femoral y empujamos
ventralmente.
First technique :
We put the patient in a prone position.
The physiotherapist is standing on the homolateral side.
We fixe the pelvis with the acetabulum with a sack.
We put our hands on the femoral head to push ventrally.
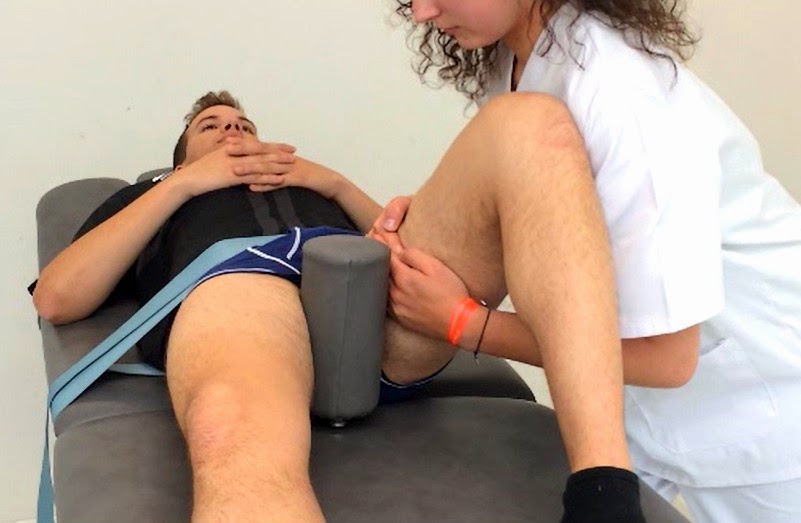
Segundo deslizamiento :
Ponemos el paciente en decubito prono con el pelvis y el tronco sobre
la camilla.
Ponemos nuestro pie para freinar su pierna.
Ponemos una cinta alrededor del muslo para sujetar el peso de la
pierna.
Ponemos nuestra mano caudal al nivel lateral y caudal del muslo.
Ponemos nuestra mana craneal sobre la cabeza femoral.
Empujamos Grado I , Grado II hasta el Grado III.
Este mobilizacion permite con un Grado III de mejorar la extension y la
rotacion externa de la articulacion coxofemoral.
Con un Grado I y II podemos testar el juego articular de la
articulacion.
Second technique :
We put the patient in a prone position pelvis and trunk positioned on
the bench
We put our foot to brake his leg.
We put a belt around the thigh of the patient to hold the limb.
The caudal hand holds the lateral and distal side of the leg.
We put the cranial hand on the femoral head.
We push from the Grade I to the Grade III
This mobilization with a Grade III allows to increase the extension and
external rotation of the hip joint.
With a Grade I and II we can test the joint play.

 Coxo valgo:
El ángulo formado por el cuello del fémur y la porción larga el huesos está aumentado (>140º)
Coxo valgo:
El ángulo formado por el cuello del fémur y la porción larga el huesos está aumentado (>140º)